
Nonspecific symptoms including headaches, chest pain, cough, sweating, nausea, and vomiting have been reported as early signs. The signs and symptoms of amniotic fluid embolism often develop rapidly. Early recognition and prompt supportive treatment are essential. Amniotic fluid embolism is a medical emergency that develops suddenly and rapidly and can be fatal. Researchers and physicians do not fully understand why amniotic fluid or fetal cells entering the mother’s bloodstream causes this reaction in some women. Breathing problems, cardiac arrest, and excessive bleeding are some of the life-threatening complications that can occur. For years, some researchers believed that the amniotic fluid and fetal cells cause obstruction within the mother’s blood vessels, but now most researchers believe that the mother’s immune system reacts to the amniotic fluid and fetal cells causing an overwhelming immune system response, which ends up harming the mother and the fetus. AFE can cause a severe, rapid decline in the mother’s health. Amniotic fluid embolism is unpredictable and no risk factors have been identified. This fluid supports, cushions, and protects a developing fetus. Amniotic fluid is contained within the amniotic sac. In this disorder, it is hypothesized that a pregnant woman has a severe, allergic reaction to amniotic fluid or other fetal material such as fetal cells, which enter the mother’s bloodstream. Stay Informed With NORD’s Email NewsletterĪmniotic fluid embolism (AFE) is an extremely rare, but life-threatening complication that affects pregnant women shortly before, during, or immediately following labor and childbirth.Find a Rare Disease Patient Organization.Find Clinical Trials & Research Studies.Launching Registries & Natural History Studies.

A Podcast For The Rare Disease Community.You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. We link primary sources - including studies, scientific references, and statistics - within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations. the placenta separating from the uterus.exposure to harmful substances, including tobacco, illicit drugs, and alcohol.medical conditions, such as lung disease and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.a urinary tract infection (UTI) or sexually transmitted infection (STI).cerclage, a procedure where doctors stitch the cervix closed until the baby is ready for delivery.the amniocentesis needle making a hole that takes too long to heal.contractions that put pressure on the amniotic sac, causing it to tear.Women who got pregnant less than 6 months after their last labor or are carrying more than one baby have a higher risk of PROM. If the amniotic sac breaks before the 37th week of pregnancy, doctors refer to it as preterm PROM. Sometimes, the amniotic sac breaks or leaks before labor starts. For most women, it is more likely to feel like a constant trickle. People often refer to this as the water breaking.Īccording to the American Pregnancy Association, just one in 10 women will experience a “dramatic gush” of amniotic fluid. The amniotic sac ruptures when a woman goes into labor. If the dye shows up on the pad, this can indicate leaking amniotic fluid. They may also perform a dye test, which involves introducing blue dye into the amniotic sac and asking the woman to wear a sanitary pad. An ultrasound can help doctors check how much fluid is surrounding the baby. These tests could include a vaginal exam to see if the cervix is dilating and the woman is in labor.

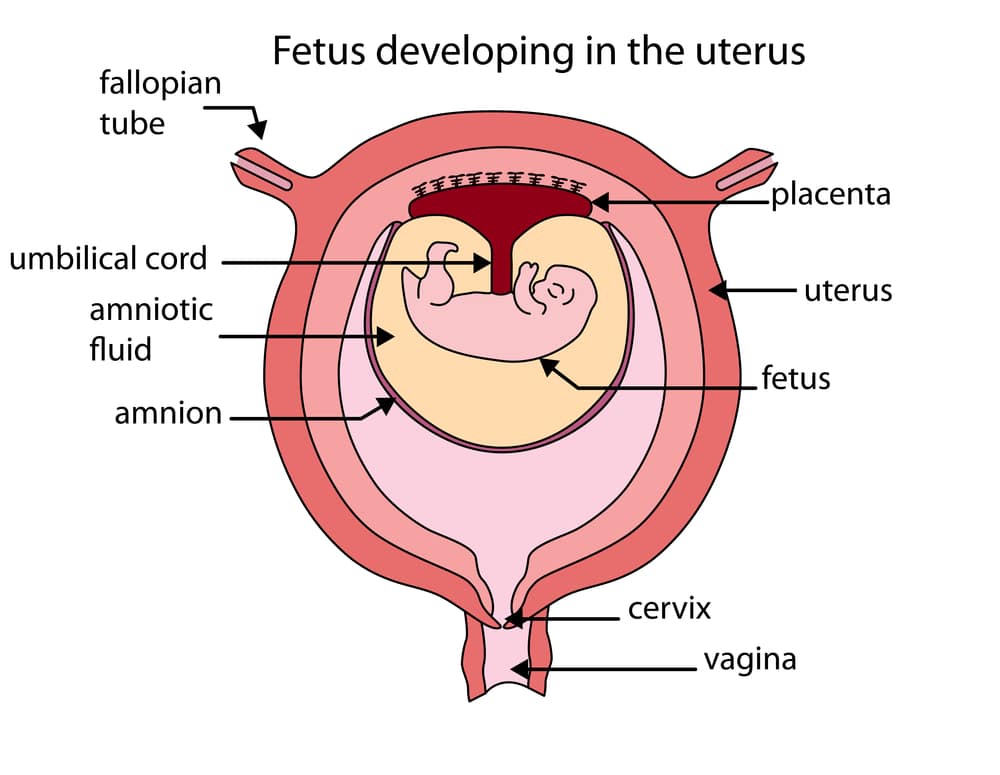
They may also carry out tests to determine the cause of the leak. While waiting for medical attention, a woman should not use tampons, have sex, or do anything else that might introduce bacteria into the vagina.Ī doctor may take a sample of the fluid to determine whether it is amniotic fluid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
